Communication from Node App to MongoDB
Summary: Communication from Node application to MongoDB.
Contents:
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Introduction to MongoDB
- 3. Installing Node MongoDB Driver Module and communicating with MongoDB
- 4. Using
Promisesto solve calback hell problem
1. Introduction
MongoDB is a document database, noSQL database.
This blog records how to install MongoDB and how to communicate from Node application with a MongoDB server.
📦mongodb
┗ 📂data
📦node-mongo
┣ 📜index.js
┣ 📜operations.js
┣ 📜package.json
┗ 📜yarn.lock
2. Introduction to MongoDB
2.1 Installation
Downloade MongoDB Community Server from here: https://www.mongodb.com/try/download/community.
Follow the instruction to install it. After installation, add folder bin to environment path.
The MongoDB Shell (mongosh) is not installed with MongoDB Server. You need to follow the mongosh installation instructions to download and install mongosh separately.
2.2 Operation
-
Create a folder named
mongodbon your computer and create a subfolder under it nameddata. -
Move to the
mongodbfolder and then start the MongoDB server by typing the following at the prompt:mongod --dbpath=data --bind_ip 127.0.0.1 -
Open another command window and then type the following at the command prompt to start the mongo REPL shell:
mongo -
At the Mongo REPL prompt, type the following commands one by one and see the resulting behavior:
db use conFusion db db.help() -
Create a collection named dishes, and insert a new dish document in the collection:
db.dishes.insertOne({ name: "pizza", description: "Test" }); -
Print out the dishes in the collection, type:
db.dishes.find().pretty();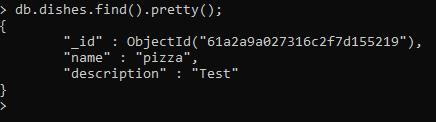
-
Learn the information encoded into the ObjectId by typing the following at the prompt:
var id = new ObjectId(); id.getTimestamp();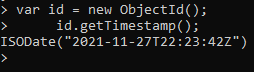
-
Drop the collection
dishes:db.dishes.drop(); -
Type
exitat the REPL prompt to exit the Mongo REPL.
3. Installing Node MongoDB Driver Module and communicating with MongoDB
-
Create a new folder named
node-mongoand move into the folder. -
At the prompt, type the following to initialize a package.json file in the node-mongo folder:
npm init -
Accept the standard defaults suggested until you end up with a
package.jsonfile, add"start": "node index"to"scripts". Thepackage.jsonlooks like below:{ "name": "node-mongo", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "Node MongoDB demo", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1", "start": "node index" }, "author": "ycheng", "license": "ISC" } -
Install the Node MongoDB driver and the Assert module by typing the following at the prompt:
npm install mongodb@3.0.10 --save npm install assert@1.4.1 --saveIf above command return errors, try
yarn:yarn add mongodb@3.0.10 yarn add assert@1.4.1 -
A Simple Node-MongoDB Application: create a new file named
index.jsand add the following code to it:const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient; const assert = require('assert'); const url = 'mongodb://localhost:27017/'; const dbname = 'conFusion'; MongoClient.connect(url, (err, client) => { assert.equal(err,null); console.log('Connected correctly to server'); const db = client.db(dbname); const collection = db.collection("dishes"); collection.insertOne({"name": "Uthappizza", "description": "test"}, (err, result) => { assert.equal(err,null); console.log("After Insert:\n"); console.log(result.ops); collection.find({}).toArray((err, docs) => { assert.equal(err,null); console.log("Found:\n"); console.log(docs); db.dropCollection("dishes", (err, result) => { assert.equal(err,null); client.close(); }); }); }); }); -
Make sure that your MongoDB server is up and running, type
yarn startornpm startat the prompt to start the server and see the result.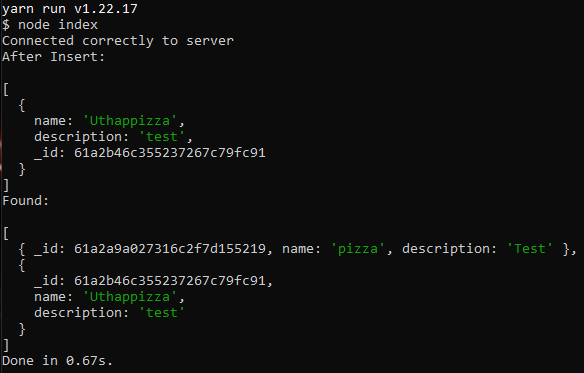
4. Using Promises to solve calback hell problem
Create file operations.js
const assert = require('assert');
exports.insertDocument = (db, document, collection, callback) => {
const coll = db.collection(collection);
return coll.insert(document);
};
exports.findDocuments = (db, collection, callback) => {
const coll = db.collection(collection);
return coll.find({}).toArray();
};
exports.removeDocument = (db, document, collection, callback) => {
const coll = db.collection(collection);
return coll.deleteOne(document);
};
exports.updateDocument = (db, document, update, collection, callback) => {
const coll = db.collection(collection);
return coll.updateOne(document, { $set: update }, null);
};
index.js
const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
const assert = require('assert');
const dboper = require('./operations');
const url = 'mongodb://localhost:27017/';
const dbname = 'conFusion';
MongoClient.connect(url).then((client) => {
console.log('Connected correctly to server');
const db = client.db(dbname);
dboper.insertDocument(db, { name: "Vadonut", description: "Test"}, "dishes")
.then((result) => {
console.log("Insert document:\n", result.ops);
return dboper.findDocuments(db, "dishes");
})
.then((docs) => {
console.log("Found Documents:\n", docs);
return dboper.updateDocument(db, { name: "Vadonut" }, { description: "Updated Test" }, "dishes");
})
.then( (result) => {
console.log("Updated Document:\n", result.result);
return dboper.findDocuments(db, "dishes");
})
.then((docs) => {
console.log("Found Updated Documents:\n", docs);
return db.dropCollection("dishes");
})
.then( (result) => {
console.log("Dropped Collection: ", result);
client.close();
})
.catch((err) => console.log(err));
})
.catch((err) => console.log(err));
Run yarn start:
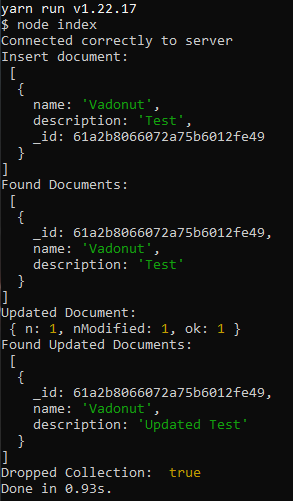

Comments